You’ve likely heard the terms “sitemap” and “indexing”, but if the technical aspects of ecommerce aren’t your forte, you may not be 100 percent certain about how these relate to you or what your sitemap does once you’ve submitted it. In this guide, we’ll address your most frequently asked questions regarding sitemaps, indexing and the basics of the robots file.
What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is visual layout of your site's structure and content, designed specifically for either search engines, humans or both. Your Volusion store's sitemap is located at www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
How is My Sitemap Generated?
Volusion automatically generates your sitemap every 24 hours. If you've recently restructured your site by adding or removing pages and want the most updated version of your site immediately, you can regenerate the sitemap manually by navigating to Marketing>>SEO and scrolling to the bottom of the page to "Sitemap".
What Information Does My Sitemap Contain?
It depends. Sitemaps can be created using HTML or XML. These are both languages search engines can understand. An HTML sitemap contains actual links to pages and can help users navigate to your products and categories in addition to creating pathways for crawlers.
Your HTML sitemaps are the product index located at www.yourdomain.com/pindex.asp and the category index located at www.yourdomain.com/cindex.asp
The XML sitemap located at www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml contains information that is only relevant to search engines. This information includes a URL to each page, its importance and the last modified date.
Why Is the Sitemap Important?
Without a sitemap, Google and other search engines will navigate through your site by following only the crawlable links. This helps search engines understand your site’s structure. But an XML sitemap provides additional information, too.
< last mod >
The last modified value lets search engines know when a page on your site was last updated. Sites that provide new, updated content regularly send positive signals to Google.
< priority >
The priority value assigns an importance on a scale of 0 - 1 to each page on your site. Your homepage has been assigned a priority of 1 while all other pages have a priority of .5. This value is relative and is only used as a signal to crawlers, not Google. It does not affect the position of your store's URLs in search results.
How Do Search Engines Find My Sitemap?
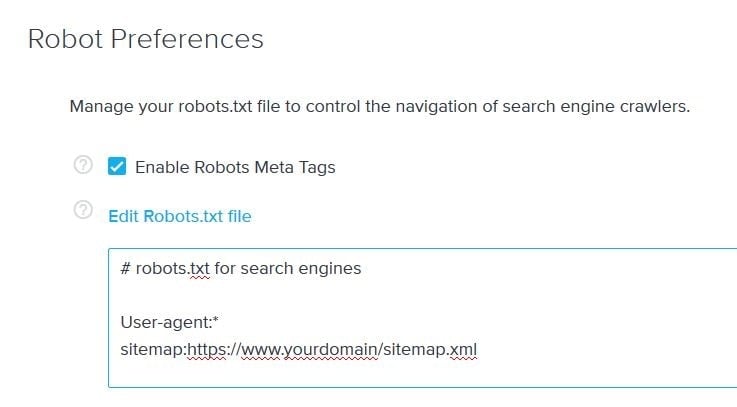
We recommend that you add your sitemap's location to your Robots.txt file, which can be edited under Marketing>>SEO. If your site has an SSL, your sitemap will be located on a secure page. It is therefore important to include "https" in your sitemap URL.
Additionally, you should submit your sitemap to search engines like Bing and Google via their Webmaster Tools Accounts. When adding new accounts, use "https" here as well.
Submitting a Sitemap to Google
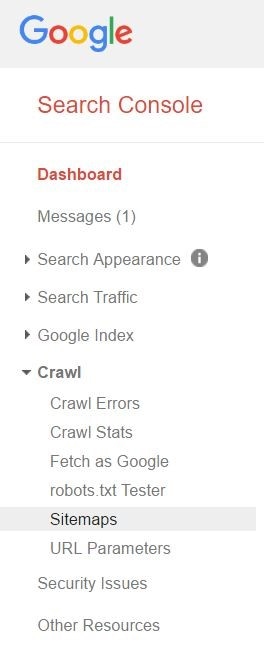
- Log in to your Webmaster account
- Click crawl>>sitemaps
- Click add/test sitemap
- Enter "sitemap.xml" into the field (without quotes)
- Submit
For more information about adding and verifying your site in Google, check out this support link.
Submitting a Sitemap to Bing
Once logged in, click "Add a Site" on the Bing Webmaster dashboard. Add your site's account information and sitemap location. You will be prompted to complete various additional steps including verifying your site.
My Sitemap Is Too Large
If your store contains more than 50,000 URLs or is larger than 10 MB, you'll be required to submit separate sitemaps. For step-by-step instructions, check out this Volusion Help Center article.
How Do I Hide Products or Categories from the Sitemap?
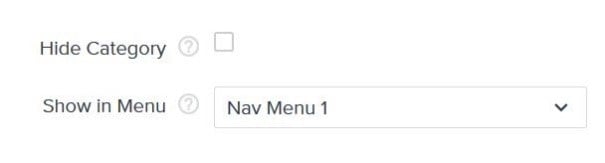

You can easily hide products or categories by utilizing the built-in "Hide" functionality. Additionally, by using the product display calendar, you can schedule when products should be displayed on your site and added to your sitemap.
Note that neither of these functionalities will prevent search engines from displaying previously indexed pages.
How Long Does it Take Search Engines to Index my Site?
Once you submit your sitemap, search engines generally take 1-2 weeks to completely index all of the URLs on your site.
My "Submitted URLs" and "Indexed URLs" Aren't the Same
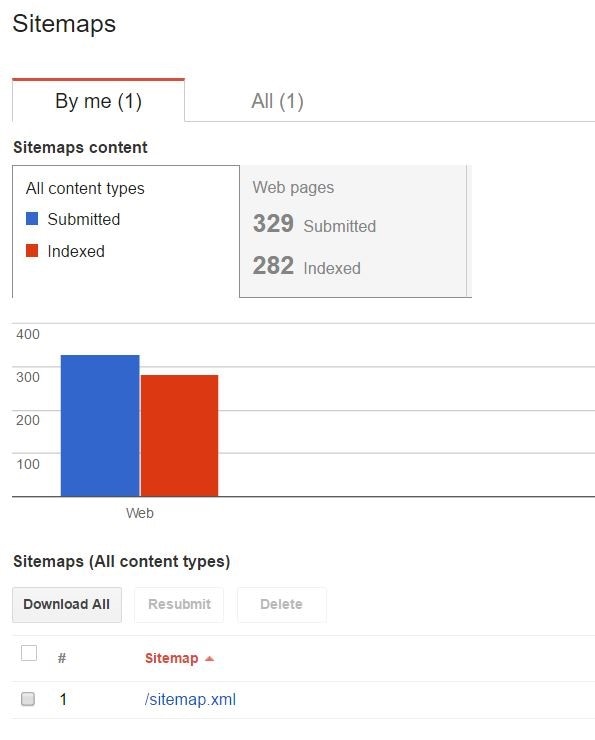
Discrepancies will always exist between these numbers, however, if a large portion of your submitted URLs are missing from the "Indexed" count, check the following:
First, ensure you've submitted your sitemap correctly. Unless you have broken your sitemap into several portions because your site contains a very high number of products, you should have only submitted one sitemap.
This sitemap's address should be http://www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml if you do not have an SSL and https://www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml if your site loads all pages securely.
Secondly, enter "site:yourdomain.com" (without quotes) into your browser's search bar to see how many results are actually returned. Google Search Console is not always 100 percent accurate, and the number of indexed URLs returned in this search may be much higher than what you see in Webmaster Tools. Additionally, ensure that there is no space between the word "site" and the colon.
Next, check your Robots.txt file under Marketing>>SEO to ensure you haven't inadvertently excluded pages you would prefer to be indexed.
And lastly, understand that while Google crawls all web pages, it does not index and display every crawled page. There are various reasons for this, which you can learn more about via this help article.
My Page Was Previously Indexed But No Longer Is
If you've Googled a series of keywords which have pulled up your site in the past and you're no longer seeing your site in the search results, there may be a number of reasons. It's likely that your page is still indexed and has simply changed position. Because Google aims to provide the best user experience by returning relevant sites by matching them to search queries, the position of your site can change frequently. Furthermore, your Google search results are not identical to the search results of the person sitting next to you. Search results are tailored to each person based on browsing history.
To further investigate whether or not Google is still indexing the page you're looking for, you can perform these two simple steps:
A. Enter "site:yourdomain.com" into your browser's search bar and look for the elusive page manually.
B. Log into Webmaster Tools and navigate to crawl>>crawl errors to look for the page here.
If the page is still being indexed but the position of your site in the search result has changed dramatically, ask yourself the following questions:
-
Have you removed or changed valuable on-page or meta content?
-
Have you restructured your site's categories?
-
Have you migrated to Volusion recently?
If your previously indexed page can no longer be found anywhere, review your Robots.txt file in Marketing>>SEO to ensure you haven't blocked pages. If you haven't blocked them, it may be possible that you have violated certain guidelines and have received a penalty. Common violations include engaging in spammy linkbuilding campaigns, having no content or unoriginal content, hiding or “cloaking” content in HTML and keyword spamming. For more information about penalties and how to remove them, check out this Google support article.
Search engines uses hundreds of on- and off-page indicators to decide which webpages should be displayed in the search results and in what position. The algorithms they utilize are complex, which means it'll take more than a functional sitemap to get into Google's good graces. To learn more about search engine optimization, check out our beginner's DIY SEO e-book or browse our support library for technical guides to SEO.











